Your vehicle’s engine is a complex and precisely engineered machine, and getting it to start smoothly is crucial for a hassle-free driving experience. At the heart of this starting process lies the starter solenoid, a small but mighty component responsible for engaging the starter motor and initiating the engine’s rotation.
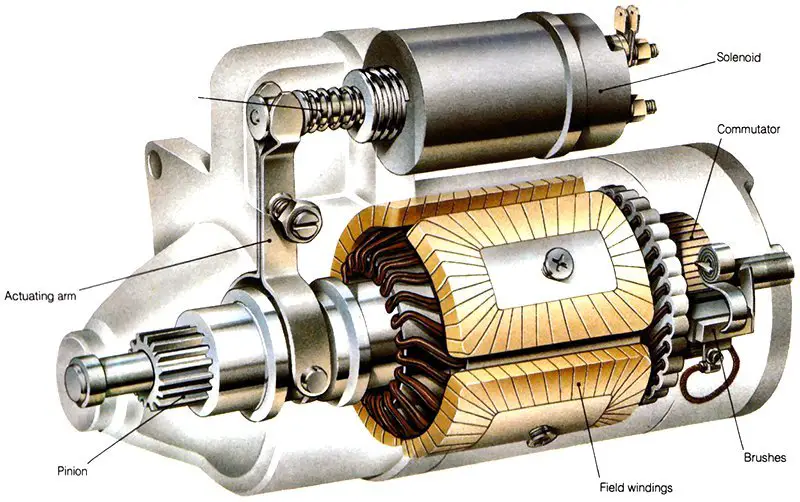
Typically, a starter solenoid features three essential connections, each requiring specific types of wires: the positive cable connected to the battery, a wire leading to the starter motor, and a slender wire originating from the ignition switch. However, if your vehicle is equipped with a 4-post starter solenoid, don’t fret. In this article, I’ll guide you through the process, including how to identify and handle the additional connection.
What Is A Starter Solenoid and Its Functions
The starter is a crucial component of the engine that is responsible for starting the engine of a vehicle. It draws electrical power from the battery and converts it into mechanical energy, which is used to turn the engine’s crankshaft and start the combustion process.
It acts as a relay switch that helps initiate the engine’s ignition process. When you turn the ignition key to start your vehicle, the starter solenoid plays a key role in completing the electrical circuit between the battery and the starter motor.
This connection allows the starter motor to engage and turn the engine over, ultimately starting the vehicle’s internal combustion engine. In essence, the starter solenoid serves as a bridge between the battery’s electrical power and the mechanical action required to crank the engine and begin the combustion process.
Here’s an explanation of what a starter solenoid is and its primary functions:
- Electromagnetic Switch: At its core, a starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch. It’s typically a cylindrical or cube-shaped device mounted on or near the vehicle’s starter motor.
- Role in the Starting Process: The starter solenoid plays a pivotal role in the starting process. When you turn the ignition key to start your vehicle, an electrical signal is sent to the starter solenoid.
- Engaging the Starter Motor: One of the main functions of the solenoid is to engage the starter motor. When the electrical signal from the ignition key is received, the solenoid uses electromagnetic force to push a plunger or lever mechanism. This action, in turn, physically engages the starter motor’s pinion gear with the engine’s flywheel or flexplate.
- Completing the Electrical Circuit: Simultaneously, the solenoid closes a set of heavy-duty electrical contacts. These contacts complete the electrical circuit between the battery and the starter motor, allowing a high current to flow from the battery to the starter motor.
- Providing High Current: The starter motor requires a substantial amount of electrical current to turn the engine over. The solenoid’s function of closing the contacts ensures that this high current is provided to the starter motor, allowing it to crank the engine.
- Safety Feature: Additionally, the starter solenoid serves as a safety feature. It prevents the starter motor from engaging if the vehicle is in gear (manual transmission) or if the transmission is not in “Park” or “Neutral” (automatic transmission). This safety mechanism prevents the vehicle from starting while it’s in gear, reducing the risk of accidents.
What Wires Go To The Starter Solenoid?
The starter solenoid in a vehicle is connected to several wires, each serving a specific function in the starting system. Here are the primary wires that go to the starter solenoid:
1. Battery Cable (Positive Terminal)
The thickest wire connected to the starter solenoid is the battery cable. This cable carries a large amount of electrical current directly from the positive terminal of the vehicle’s battery. It provides the necessary power to crank the engine when the starter is engaged.
2. Starter Motor Wire
The starter motor wire is typically a thinner wire connected to the solenoid. This wire is responsible for carrying the electrical current from the solenoid to the starter motor itself. When the solenoid engages, it completes the circuit between the battery and the starter motor through this wire, causing the starter motor to turn.
3. Ignition Switch Wire
Another wire connected to the starter solenoid is the ignition switch wire. This wire carries the electrical signal from the vehicle’s ignition switch to the solenoid. When you turn the ignition key to the “Start” position, it sends a signal through this wire to activate the solenoid.
4. Neutral Safety Switch Wire (Automatic Transmission)
In vehicles with automatic transmissions, there is typically a wire connected to the starter solenoid from the neutral safety switch. The neutral safety switch ensures that the vehicle can only be started when the transmission is in “Park” or “Neutral.” This wire prevents the starter from engaging if the transmission is in any other gear, enhancing safety.
5. Clutch Safety Switch Wire (Manual Transmission)
In vehicles with manual transmissions, there may be a wire connected to the starter solenoid from the clutch safety switch. This switch ensures that the starter can only engage when the clutch pedal is depressed. It prevents accidental starting while the vehicle is in gear.
These are the main wires that are typically connected to the starter solenoid. It’s important to note that the exact configuration and wire colors may vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
When working on your vehicle’s starting system or replacing the starter solenoid, always refer to the vehicle’s service manual or wiring diagrams to ensure proper connections and safety.
What Are Terminals On The Starter?
The starter motor in a vehicle typically has several terminals or connection points that serve different functions. These terminals are crucial for the proper operation of the starter and the starting system as a whole.
Here are the common terminals found on a starter motor:
1. Battery Terminal (B+ or BAT): This terminal is the main connection point for the positive (red) battery cable. It receives power directly from the vehicle’s battery. When the ignition key is turned to the “Start” position, the battery terminal carries electrical current from the battery to the starter motor to initiate engine cranking.
2. Starter Motor Terminal (M or ST): The starter motor terminal is connected to the starter motor itself. When the starter solenoid engages, it allows electrical current to flow from this terminal to the starter motor. This current causes the starter motor to turn, cranking the engine.
3. Ignition Switch Terminal (S or SOL): The ignition switch terminal is connected to the vehicle’s ignition switch. When you turn the ignition key to the “Start” position, it sends an electrical signal to this terminal. This signal activates the starter solenoid, which in turn connects the battery terminal to the starter motor terminal, allowing current flow to start the engine.
4. Ground Terminal (GND or GRD): The ground terminal is the connection point for the starter motor’s ground or negative cable. It provides a path for electrical current to return from the starter motor to the vehicle’s battery, completing the electrical circuit.
5. Over-Crank Protection Terminal (optional): Some starters may have an additional terminal for over-crank protection. This terminal is connected to a sensor that monitors the engine’s cranking speed. If the engine doesn’t start after a certain number of cranking attempts, this terminal can prevent further cranking to avoid damage to the starter and the engine.
These terminals are crucial for the proper functioning of the starter motor and the starting system. Each terminal serves a specific purpose, from receiving power from the battery to engaging the starter motor and ensuring that cranking only occurs when the ignition key is in the “Start” position.
When working on the starter or its wiring, it’s essential to know the function of each terminal and make the correct connections to ensure reliable engine starting.
Where Do The Wires Go On A Starter Solenoid?
The wires on a starter solenoid connect to specific terminals or posts, each serving a different function in the starting system. Here’s where the wires typically go on a starter solenoid:
- Battery Cable (Positive): This is usually the thickest wire and is typically red. It connects to the large terminal labeled “B,” “BATT,” or “+.” This wire comes directly from the positive terminal of the vehicle’s battery. It supplies high current from the battery to the starter motor.
- Starter Motor Wire: This wire is often smaller and may be red or black. It connects to the smaller terminal labeled “M” or “ST” on the starter solenoid. This wire carries current from the solenoid to the starter motor itself, causing the starter motor to turn when the solenoid engages.
- Ignition Switch Wire: This wire is usually thinner and is connected to the smaller terminal labeled “S” or “SOL.” It comes from the ignition switch. When you turn the ignition key to the “Start” position, it sends an electrical signal through this wire to the solenoid. This signal activates the solenoid, which, in turn, connects the battery cable to the starter motor wire, allowing current flow to start the engine.
- Ground Wire: The ground wire serves as the return path for electrical current and is connected to the starter motor’s housing or another ground point on the vehicle. It ensures that the starter motor has a complete electrical circuit.
Please note that the specific labeling of terminals and wire colors may vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model. It’s crucial to consult your vehicle’s service manual or wiring diagram to identify the correct terminals and wire connections for your particular vehicle’s starter solenoid.
Additionally, when working on the electrical system of your vehicle, exercise caution, and disconnect the battery to prevent electrical accidents.
Safety Tips When Working With Starter Solenoid Wires
Working with starter solenoid wires involves dealing with the electrical system of your vehicle, which can pose potential safety hazards. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind when working on starter solenoid wires:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before you begin any work on the electrical system, always disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This step is crucial to prevent accidental electrical shock or short circuits. Disconnect the negative (black) terminal first and then the positive (red) terminal.
- Use Proper Tools: Ensure you have the right tools for the job, including insulated pliers and screwdrivers. Using tools with insulated handles can help prevent accidental electrical contact.
- Wear Safety Gear: Consider wearing safety gear such as safety glasses and gloves. These can protect your eyes and hands from potential hazards.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: If you’re working in an enclosed space, ensure there’s proper ventilation. This is especially important if you’re dealing with gasoline or other flammable substances near the starter solenoid.
- Inspect Wires and Connections: Before making any connections or repairs, inspect the wires and connections for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any damaged components to ensure a safe and reliable electrical connection.
- Follow Wiring Diagrams: Consult your vehicle’s service manual or wiring diagram to identify the correct wires and terminals. Misconnecting wires can lead to electrical problems or, in some cases, vehicle damage.
- Avoid Short Circuits: Be cautious not to accidentally create a short circuit by allowing exposed wires or tools to touch other metal parts of the vehicle. A short circuit can lead to electrical fires or damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Double-Check Connections: After making any wire connections, double-check that all connections are secure and properly insulated. Loose or exposed wires can cause electrical problems or accidents.
- Test Before Assembly: Before reassembling any components, test the starter solenoid and starter motor to ensure they function correctly. This can help you identify and address any issues before completing the job.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about working with electrical systems or lack experience, it’s best to seek the assistance of a qualified automotive technician. They have the expertise and tools to safely diagnose and repair electrical issues.
We’ve explored the functions of the starter solenoid and its terminals, delving into the wires that are typically associated with this component. Whether it’s the battery cable, ignition switch wire, or starter motor wire, each serves a distinct purpose in the starting process.


